Introduction
In recent years, the urgency to address environmental challenges and combat climate change has led to a rapid surge in the development and adoption of green technology. Green technology, also known as clean technology or cleantech, refers to the use of innovative solutions and practices that aim to minimize environmental impact, conserve resources, and promote sustainability. These advancements across various sectors are revolutionizing the way we produce and consume energy, manage waste, conserve water, and build a greener and more sustainable future for generations to come.
Renewable Energy
One of the most prominent areas of green technology is the development and utilization of renewable energy sources. Traditional fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. However, renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass offer clean alternatives that are abundant, widely available, and produce little to no emissions during operation.
Solar power, for instance, has seen significant advancements in technology, making it more efficient and cost-effective than ever before. The use of photovoltaic (PV) cells has become increasingly common, allowing solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity. The integration of solar power into residential, commercial, and industrial applications has paved the way for decentralized and sustainable energy generation.
Wind power has also experienced remarkable growth, with the development of larger and more efficient turbines. Offshore wind farms, situated in open waters, harness strong and consistent wind currents to generate electricity on a massive scale. These renewable energy sources not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also create job opportunities, promote energy independence, and contribute to the reduction of carbon emissions.
Energy Storage
A key challenge in integrating renewable energy sources into our power grid is the intermittent nature of wind and solar power. Energy storage technologies play a crucial role in overcoming this hurdle by storing excess energy during periods of high production and releasing it when demand exceeds supply. This ensures a consistent and reliable supply of electricity.
Advancements in battery technology, particularly lithium-ion batteries, have revolutionized energy storage. These batteries are now widely used in electric vehicles, residential and commercial energy storage systems, and grid-scale applications. Moreover, research is underway to develop more sustainable and efficient alternatives, such as solid-state batteries and flow batteries, that have the potential to store larger amounts of energy and reduce reliance on scarce resources.
Smart Grid and Energy Efficiency
Green technology is transforming the way we manage and distribute energy through the implementation of smart grids. A smart grid uses advanced sensors, communication networks, and data analytics to optimize energy generation, transmission, and consumption. It enables real-time monitoring and control, improving grid reliability, efficiency, and resilience.
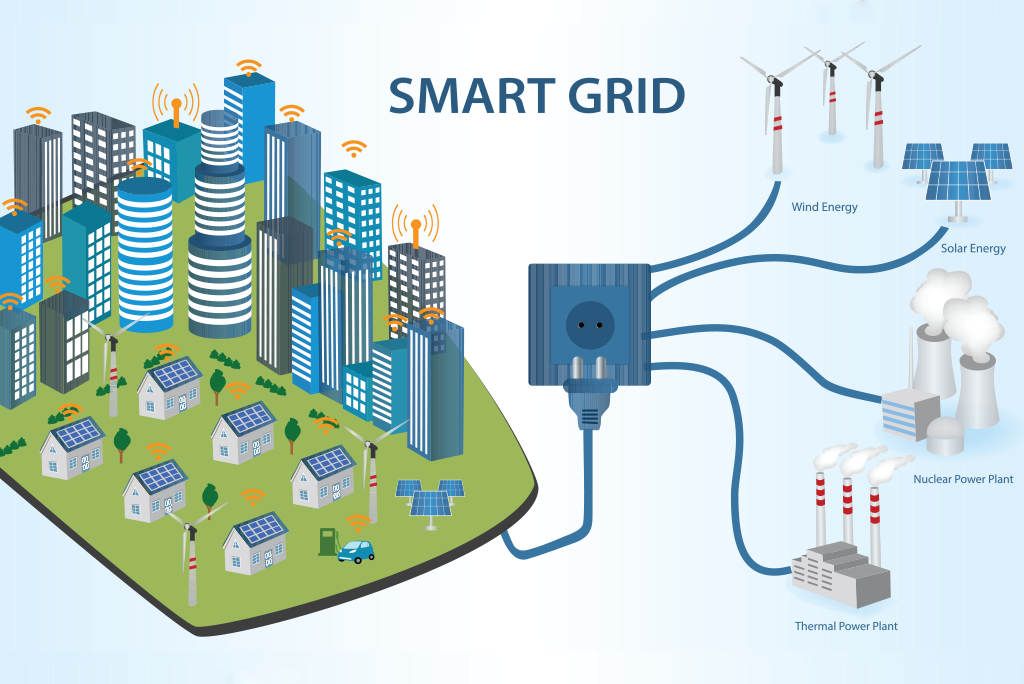
Furthermore, energy efficiency plays a critical role in achieving a sustainable future. Green technology solutions focus on reducing energy waste and maximizing the efficiency of appliances, buildings, and industrial processes. Smart thermostats, LED lighting, energy-efficient appliances, and intelligent building management systems are just a few examples of innovations that help conserve energy and lower carbon footprints.
Waste Management and Circular Economy
Another vital aspect of green technology is waste management and the promotion of a circular economy. Traditional linear models of production and consumption, characterized by a “take-make-dispose” approach, result in excessive waste generation and resource depletion.
Green technology aims to shift towards a circular economy, where waste is minimized, materials are recycled or reused, and resources are conserved. Innovations such as waste-to-energy technologies, anaerobic digestion, and composting systems allow for the conversion of organic waste into renewable energy or nutrient-rich fertilizers. Recycling processes have also become more efficient, enabling the recovery of valuable materials from electronic waste, plastics, and other discarded products.
Sustainable Transportation
Transportation is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Green technology is driving the development of sustainable transportation solutions to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote cleaner alternatives.
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained widespread attention and adoption. With advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure, EVs offer zero-emission transportation options. Furthermore, research and development efforts are focused on enhancing battery range, reducing charging time, and increasing the availability of charging stations.
Additionally, the concept of shared mobility, including ride-sharing, bike-sharing, and car-sharing, has gained momentum, reducing the number of vehicles on the road and promoting efficient use of resources.
Conclusion
Green technology is at the forefront of the global movement towards a sustainable future. With innovations in renewable energy, energy storage, smart grids, waste management, and sustainable transportation, we have the tools to mitigate climate change, conserve resources, and protect the environment.
Governments, businesses, and individuals must continue to invest in and support the development and implementation of green technology solutions. By embracing these innovations, we can create a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable world for present and future generations. The time to act is now, as we have the power to shape the future and secure a better planet for all.

