In recent years, the field of robotics has made significant advancements, and its impact on various industries cannot be overstated. One area where robotics has particularly shone is medicine. With the convergence of technology and healthcare, robotics has emerged as a powerful tool in revolutionizing the way medical procedures are performed, diagnoses are made, and patient care is delivered. From surgical robots to assistive devices, robotics has the potential to transform healthcare and improve patient outcomes in ways we never thought possible.
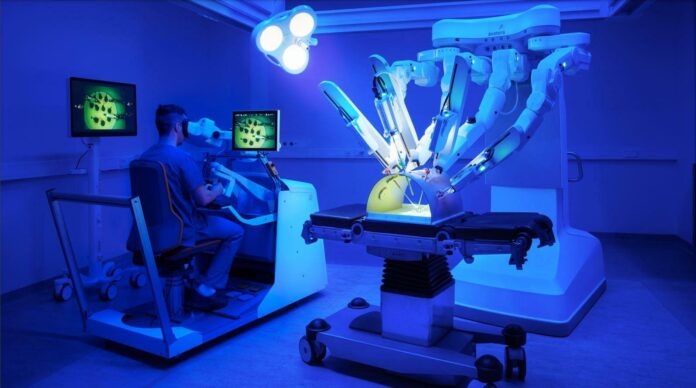
One of the most significant contributions of robotics in medicine is in the field of surgery. Surgical robots have become increasingly prevalent in operating rooms, allowing surgeons to perform intricate procedures with enhanced precision and dexterity. These robots, often controlled by skilled surgeons, offer several advantages over traditional methods. For instance, they can access difficult-to-reach areas within the body, reducing the need for invasive surgeries. With the aid of robotic arms and specialized instruments, surgeons can perform minimally invasive procedures, leading to smaller incisions, reduced scarring, and faster recovery times for patients.
Moreover, surgical robots provide surgeons with real-time, high-definition imaging, enabling them to visualize the surgical site in exceptional detail. This enhanced visualization allows for more accurate and precise movements, minimizing the risk of errors and complications. Additionally, the use of robotic assistance in surgery decreases the surgeon’s fatigue, as the machines can take on repetitive tasks and perform them flawlessly, freeing up the surgeon to focus on critical decision-making during the procedure.
Another area where robotics is making waves in healthcare is in rehabilitation and assistive devices. Individuals with mobility impairments or disabilities can greatly benefit from robotic exoskeletons and prosthetics. These devices provide support and assistance to patients, helping them regain independence and mobility. Robotic exoskeletons, for example, can enable individuals with spinal cord injuries to walk again, improving their quality of life and promoting physical and psychological well-being. Prosthetic limbs equipped with robotics and artificial intelligence are becoming increasingly advanced, allowing users to perform complex movements and tasks that were once unimaginable.
Beyond the operating room and rehabilitation, robots are also finding applications in healthcare settings, such as hospitals and care facilities. Autonomous robots are being used for tasks like sterilizing hospital rooms, delivering medications, and assisting in patient monitoring. These robots can help reduce the risk of infections by ensuring thorough sanitization and minimize the workload of healthcare staff, allowing them to focus on direct patient care. Furthermore, robots can be programmed to collect and analyze patient data, providing valuable insights to healthcare professionals for early detection of diseases and personalized treatment plans.

The integration of robotics in medicine, however, does not seek to replace healthcare professionals. Instead, it aims to augment their skills and expertise, enhancing patient care and outcomes. The collaboration between humans and robots can lead to a synergy of strengths, combining the precision and tirelessness of machines with the critical thinking and empathy of healthcare providers. By offloading repetitive tasks to robots, healthcare professionals can dedicate more time to building relationships with patients, making informed decisions, and providing compassionate care.
While the advancements in robotics have shown immense promise, there are still challenges to address. One significant hurdle is the cost associated with implementing robotic systems in healthcare facilities. The initial investment and ongoing maintenance expenses can be substantial, limiting their accessibility to some healthcare institutions. However, as technology continues to evolve and become more affordable, the adoption of robotics in medicine is expected to become more widespread.
Another concern is the ethical considerations surrounding the use of robots in healthcare. Questions regarding patient privacy, data security, and the potential for automation to replace human touch and empathy must be carefully examined. Striking the right balance between technological advancements and preserving the human element in healthcare is crucial to ensure that robotics complements and enhances the patient-provider relationship rather than eroding it.
In conclusion, robotics is playing a transformative role in medicine, revolutionizing healthcare in multiple ways. From assisting surgeons in performing precise and minimally invasive procedures to providing support and mobility to individuals with disabilities, robotics is reshaping the landscape of healthcare. The integration of robots in hospitals and care facilities is streamlining tasks, improving patient outcomes, and optimizing resource utilization. However, it is essential to navigate the challenges and ethical considerations associated with robotics to ensure that the technology is leveraged responsibly and with the ultimate goal of providing the best possible care to patients. As technology continues to advance, we can expect robotics to continue pushing the boundaries of medicine, opening up new possibilities for improved healthcare delivery in the future.