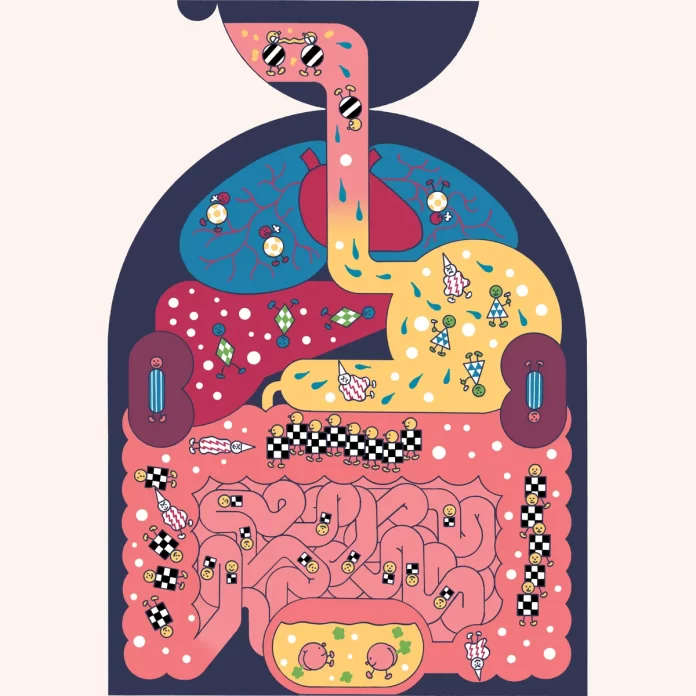
The human body is a complex and intricate system that hosts trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the human microbiome. These tiny organisms, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microbes, reside in various parts of our body, such as the skin, mouth, gut, and reproductive tract. They form a dynamic internal ecosystem that plays a vital role in our overall health and well-being.
For many years, the microbiome remained largely unexplored, but recent advancements in scientific research and technology have shed light on its significance. We now understand that the human microbiome is not merely a collection of random microbes but a highly organized and interconnected network that interacts with our body in numerous ways.
The gut microbiome, in particular, has garnered significant attention due to its central role in our health. It consists of trillions of bacteria that inhabit our digestive tract, with over a thousand different species identified so far. These bacteria perform a wide range of functions, such as aiding in digestion, synthesizing vitamins, metabolizing drugs, and modulating our immune system.
One of the key functions of the gut microbiome is its involvement in digestion and nutrient absorption. The bacteria present in our gut break down complex carbohydrates and fiber that our own body enzymes cannot digest. This process produces short-chain fatty acids, which serve as an essential energy source for the cells lining our intestine. Additionally, the gut microbiome helps in the absorption of nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, promoting overall nutritional status.
The gut microbiome also plays a crucial role in regulating our immune system. It acts as a barrier against harmful pathogens by occupying the available space and resources in our gut, making it more challenging for pathogens to establish themselves. Furthermore, the gut microbiome interacts with immune cells, training and shaping them to respond appropriately to threats while preventing excessive inflammation or autoimmune reactions.

Moreover, emerging research suggests that the gut microbiome may have an impact on our mental health. The gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication pathway between the gut and the brain, enables the exchange of information via chemical messengers. Certain microbes in the gut can produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which play a crucial role in regulating mood, anxiety, and stress levels. Imbalances in the gut microbiome have been linked to mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and even neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Aside from the gut, the skin microbiome also holds importance in maintaining our health. The skin is home to a diverse array of microbes that form a protective barrier against harmful invaders. These microbes compete with potential pathogens, preventing their colonization and promoting a healthy balance. However, disruptions in the skin microbiome can lead to various dermatological conditions, such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis.
The oral microbiome, too, plays a crucial role in our overall well-being. It influences dental health by contributing to the formation of dental plaque and the prevention of tooth decay and gum disease. Moreover, imbalances in the oral microbiome have been linked to systemic health issues like cardiovascular disease, respiratory infections, and preterm birth complications.
Given the significance of the human microbiome, maintaining its balance and diversity is crucial. Unfortunately, several factors in our modern lifestyle can disrupt the microbiome. Antibiotics, for instance, are essential for treating bacterial infections but can also disturb the natural balance of bacteria in our gut. Poor dietary choices, stress, lack of sleep, and excessive hygiene practices can also negatively impact the microbiome.
To support a healthy microbiome, it is essential to adopt practices that promote microbial diversity. Consuming a balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods like yogurt and kimchi can provide prebiotics and probiotics that nourish the beneficial bacteria in our gut. Avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use, managing stress, getting adequate sleep, and maintaining good oral hygiene are also crucial for a thriving microbiome.
The study of the human microbiome is still in its early stages, and there is much more to learn about this complex ecosystem within us. However, it is evident that the microbiome is not just a passive inhabitant of our body but an active participant in our health and well-being. By understanding and nurturing our microbiome, we can unlock new possibilities for preventing and treating various diseases, improving our digestive health, enhancing our mental well-being, and promoting overall vitality.