Sleep is a fundamental aspect of human life, yet its intricacies and profound effects on our overall well-being remain a subject of ongoing scientific exploration. While we may perceive sleep as a passive state of rest, researchers have uncovered a wealth of knowledge about its active role in various physiological and cognitive processes. From memory consolidation to emotional regulation, the importance of sleep cannot be overstated. In this article, we will delve into the science of sleep, unraveling its significance and exploring its effects on our daily lives.
Understanding Sleep Cycles:
To comprehend the science behind sleep, we first need to understand its underlying structure. Sleep is characterized by recurring cycles, consisting of two main stages: non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. NREM sleep is further divided into three stages: N1, N2, and N3.
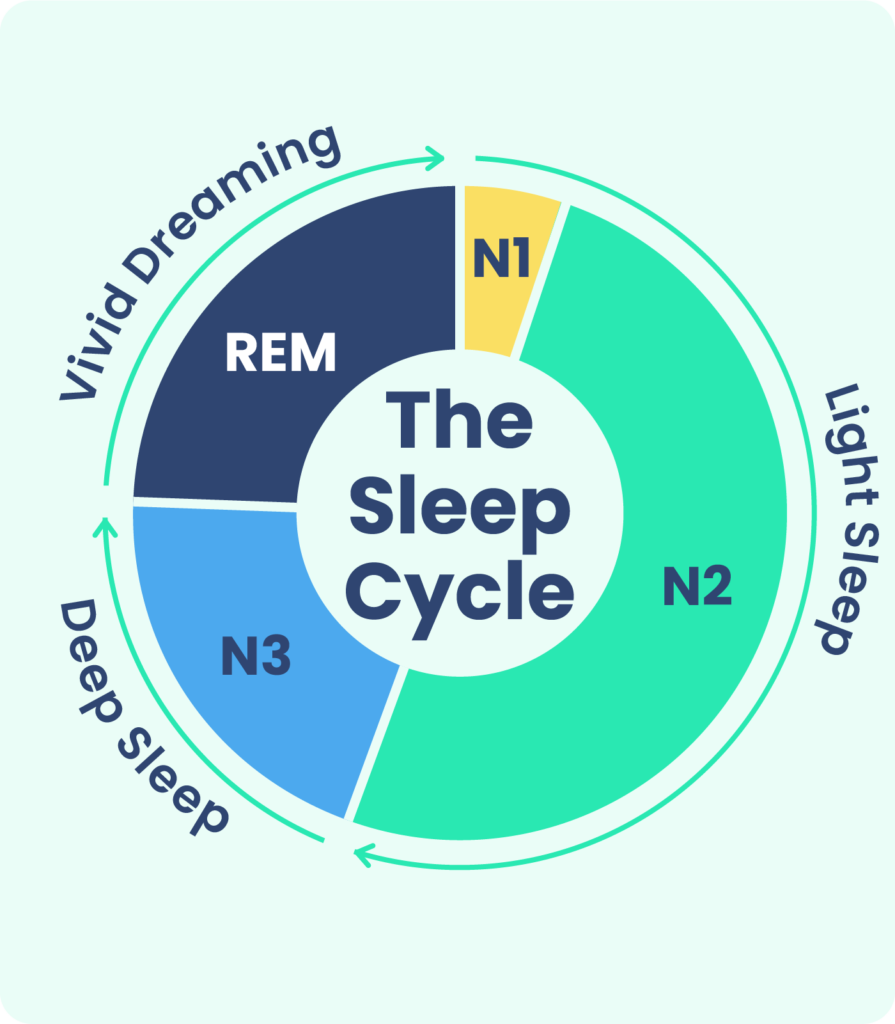
N1 marks the transition from wakefulness to sleep, and it is considered a light sleep stage. In N2, the body relaxes further, and brain activity slows down, with occasional bursts of rapid brain waves known as sleep spindles. N3, also known as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep (SWS), is the stage where the body repairs and regenerates itself.
REM sleep, on the other hand, is the stage where dreams occur. During this stage, brain activity increases, and our eyes move rapidly beneath our eyelids. REM sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation and emotional regulation.
The Importance of Sleep:
Sleep is not merely a period of inactivity. It serves vital functions necessary for our physical and mental well-being. Let’s explore some of the essential roles sleep plays in our lives.
Memory Consolidation: Sleep plays a pivotal role in consolidating memories and enhancing learning. During REM sleep, the brain processes and stores information gathered throughout the day, reinforcing neural connections and aiding memory recall.
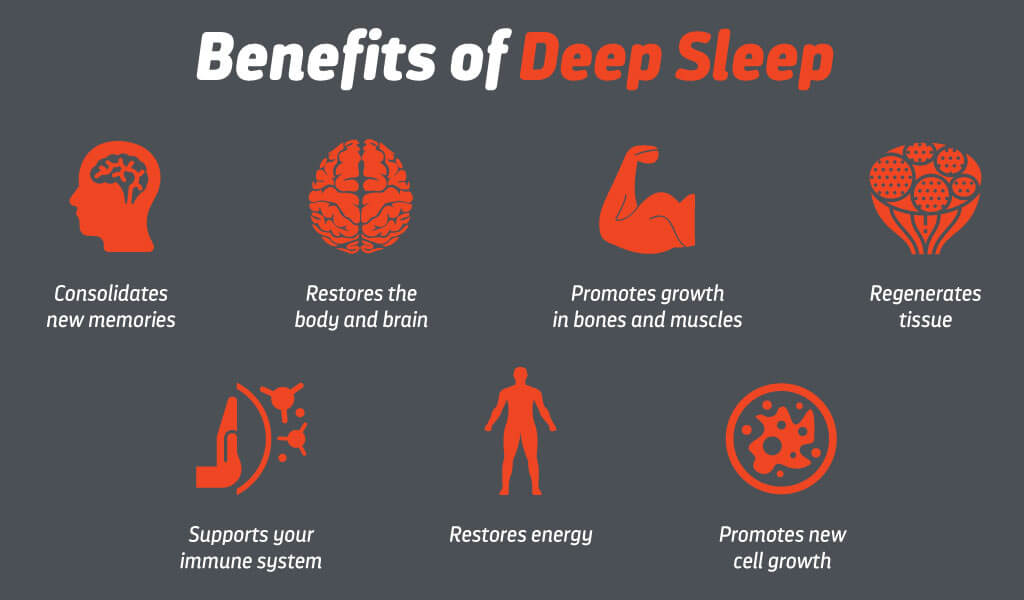
Physical Restoration: Deep sleep (N3) promotes physical restoration by facilitating tissue repair, muscle growth, and hormone regulation. It is during this stage that the body releases growth hormone, necessary for development and overall health.
Cognitive Function: A good night’s sleep is crucial for optimal cognitive function. Sleep deprivation has been linked to impaired attention, concentration, decision-making, and problem-solving abilities. Sufficient sleep enhances creativity, critical thinking, and overall cognitive performance.
Emotional Regulation: Sleep plays a significant role in emotional well-being. Insufficient sleep can lead to increased emotional reactivity, irritability, and difficulty regulating emotions. It is during REM sleep that the brain processes and regulates emotional experiences, allowing us to maintain emotional balance.
Immune Function: Sleep is closely intertwined with our immune system. During sleep, the body releases cytokines, proteins that help fight off infection, inflammation, and stress. Sleep deprivation weakens the immune system, making us more susceptible to illnesses.
Effects of Sleep Deprivation:
In today’s fast-paced world, sleep deprivation has become a prevalent issue. Chronic sleep deprivation can have far-reaching effects on our physical and mental health. Let’s explore some of the consequences of sleep deprivation:
Impaired Cognitive Performance: Lack of sleep impairs attention, concentration, and memory, making it challenging to learn and retain information. It hampers problem-solving abilities, creativity, and critical thinking skills.
Increased Risk of Chronic Conditions: Sleep deprivation has been linked to a higher risk of developing chronic conditions such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and weakened immune system functioning. It disrupts the balance of hormones responsible for appetite regulation and glucose metabolism.
Mental Health Issues: Lack of sleep is closely associated with mental health problems such as anxiety and depression. Sleep deprivation can exacerbate existing mental health conditions and increase the risk of developing new ones.

Reduced Motor Skills: Sleep deprivation impairs motor skills, reaction times, and hand-eye coordination, leading to an increased risk of accidents and injuries. Sleep-deprived individuals may experience microsleep episodes, brief moments of involuntary sleep, impairing their ability to stay alert.
Emotional Instability: Sleep deprivation can lead to heightened emotional reactivity, irritability, mood swings, and decreased emotional resilience. It impairs our ability to regulate emotions effectively, leading to strained relationships and decreased overall well-being.
Tips for Better Sleep:
Given the importance of sleep, it is crucial to prioritize good sleep hygiene to reap its numerous benefits. Here are some tips for better sleep:
Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep quality.
Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment: Make sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Use comfortable bedding, invest in a supportive mattress, and consider using white noise machines or earplugs to block out disturbances.

Establish a Bedtime Routine: Engage in relaxing activities before bed, such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation. Establishing a consistent routine signals your body that it’s time to wind down.
Limit Stimulants and Electronics: Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and heavy meals close to bedtime. Additionally, minimize exposure to electronic devices that emit blue light, as it can disrupt your sleep-wake cycle. Consider implementing a digital curfew before bed.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can promote better sleep. However, avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as it can increase alertness and make it harder to fall asleep.
Conclusion:
The science of sleep unravels the significance of this fundamental aspect of our lives. From memory consolidation to emotional regulation, sleep plays a crucial role in our physical and mental well-being. Understanding the importance of sleep and implementing healthy sleep habits can lead to improved cognitive function, emotional stability, and overall quality of life. Prioritizing sleep is not a luxury but a necessity for optimal health and well-being.

